Contact Us
Other Articles
2. What is Chemotherapy?
3. What is Radiotherapy?
4. Role of Ayurveda in Cancer Treatment
5. Genesis of Cancer
6. Early Detection of Cancer
7. Diet, Nutrition & Cancer
8. Tobacco Smoking & Cancer
9. Conventional Treatment of Cancer
10. Soft Tissue Sarcoma
11. Mesothelioma
12. Skin Cancer
13. Bone Cancer
14. Leukaemia
15. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL)
16. Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia (CML)
17. Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia (ALL) & Acute Non-Lymphocytic Leukaemias (ANLL)
18. Acute Myelogenous Leukaemia (AML)
19. Lymphoma
20. Multiple Myeloma
21. Breast Cancer
22. Prostate Cancer
23. Oral Cancer (Carcinoma of the Cheek, Lips & Tongue)
24. Carcinoma of the Salivary Gland
25. Carcinoma of the Paranasal Sinus
26. Carcinoma of Pharynx (Oropharynx, Nasopharynx and Hypopharynx)
27. Carcinoma of the Larynx
28. Brain & Spinal Cord Tumours
29. Primary Tumours of the Brain
30. Metastases in the Brain
31. Carcinoma of the Oesophagus
32. Thyroid Cancer
33. Bronchogenic Carcinoma (Lung Cancer)
34. Secondary Cancers of the Lung
35. Carcinoma of the Stomach
36. Liver Cancer
37. Gallbladder & Biliary Tract Cancer
38. Pancreatic Cancer
39. Kidney Cancer (Renal Cell Carcinoma and Nephroblastoma)
40. Urinary Tract (Transitional Cell Carcinoma) & Bladder Cancer
41. Carcinoma of Colon & Rectum
42. Primary Tumours of the Testis
43. Ovarian Cancer (Stromal, Germ Cell and Krukenberg's Tumour)
44. Carcinoma of Uterus
45. Cervix Cancer
46. Paediatric Cancers
47. AIDS Related Cancers
48. Carcinoma of Unknown Primary Site (CUPS)
49. Role of Nutrition in Cancer Treatment
50. Chinese Medicine in Cancer Treatment
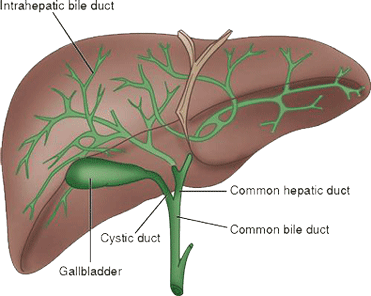
Carcinoma of the gallbladder has a threefold higher incidence in females as compared to males. It usually affects elderly women. About 80 percent cases of the gallbladder carcinoma are found to have gallbladder stones, although most of the people who have gallstones may not develop the gallbladder cancer. Carcinoma of the biliary tract, arising from ductular cells of the biliary tree, is known as cholangiocarcinoma. Common extrahepatic sites of the cholangiocarcinoma are the gallbladder and the junction of right & left hepatic ducts.
Carcinoma of the gallbladder & biliary tract usually present with:
- Obstructive jaundice
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Chills
- Pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen
- Enlarged tender liver
- Haematemesis
- Occult blood in the stool
Carcinoma of the gallbladder may invade the adjacent tissues. Spread to
the peritoneum may lead to ascites. There may be the formation of a fistula between
the biliary system and the adjacent organs leading to various complications.
Carcinoma of the gallbladder is usually detected incidentally after
cholecystectomy operation, done for gallbladder stones.
Staging of carcinoma of the gallbladder is done as follows:
- In localised resectable stage of the gallbladder carcinoma, the tumour is confined to the gallbladder and it can be completely removed by surgery.
- In the unresectable stage of the gallbladder carcinoma, the tumour cannot be removed completely by surgery. Gallbladder carcinoma is usually detected in the unresectable stage.
- Recurrent carcinoma of the gallbladder is the one that reappears after an apparent recovery in response to the initial treatment.
Procedures used in diagnosis and evaluation of the gallbladder carcinoma
include X-rays, ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
(PTC), endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), laparoscopy and
biopsy.
Disclaimer:
This content is for information and educational purposes only and should not be perceived as medical advice. Please consult a certified medical or healthcare professional before making any decision regarding your health using the content above.
Click here to go back to the list of all Articles
Add New Comment
-
 Shailaja
Shailaja
Can concentrate be given to gall bladder cancer patient undergoing chemotherapy Cancertame Private Limited
Cancertame Private Limited
Dear Shailaja, Your query has been replied to by our support team on the Email ID provided by you, for any other query you can write us back at support@cancertame.com Regards, Support Team
25 Aug 2019



Gallbladder & Biliary Tract Cancer